Frontline Digital Transformation
23 min read
The Most Common 8 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing & How to Manage Resources

Manufacturing is all about making the highest quality products at the lowest cost. Reaching that goal means searching for and eliminating causes of wasted time, wasted materials, and wasted effort.
Table of Contents
1. Overview of the 8 Wastes in Lean Manufacturing
2. Challenges of Lean Manufacturing & Resource Optimization
3. Tips for Implementing Lean Manufacturing
4. Benefits of Effective Lean Manufacturing & Resource Optimization
5. Strategies for Effective Resource Management & Lean Manufacturing
6. Applying the 5S Methodology for Workplace Organization & Efficiency
8. Just-in-Time (JIT) Production & Inventory
9. The Importance in Employee Training and Development
10. Tools & Techniques to Support Lean Manufacturing
In the 1950s and 1960s, the Japanese created their new and improved Toyota Production System and implemented changes designed to do more with less. That system has developed into what we call “lean manufacturing” and is still used in manufacturing facilities worldwide.
Lean manufacturing is a production method that aims to reduce waste and increase efficiency. Lean manufacturing strives for continuous improvement using tools like kaizen, which translates to “change for the better,” and just-in-time manufacturing.
By identifying and eliminating the waste of lean manufacturing, companies can cut costs without affecting the value for the customer.
Studies show that 20% of every dollar spent in manufacturing goes to waste. That accounts for up to $8 trillion in yearly losses or 10% of the GWP. So, companies should look for ways to reduce that 20% loss by enacting better systems.

This article will discuss lean manufacturing techniques and provide valuable tips on implementing lean within an organization while using resources the most effectively.
Overview of the 8 Wastes in Lean Manufacturing
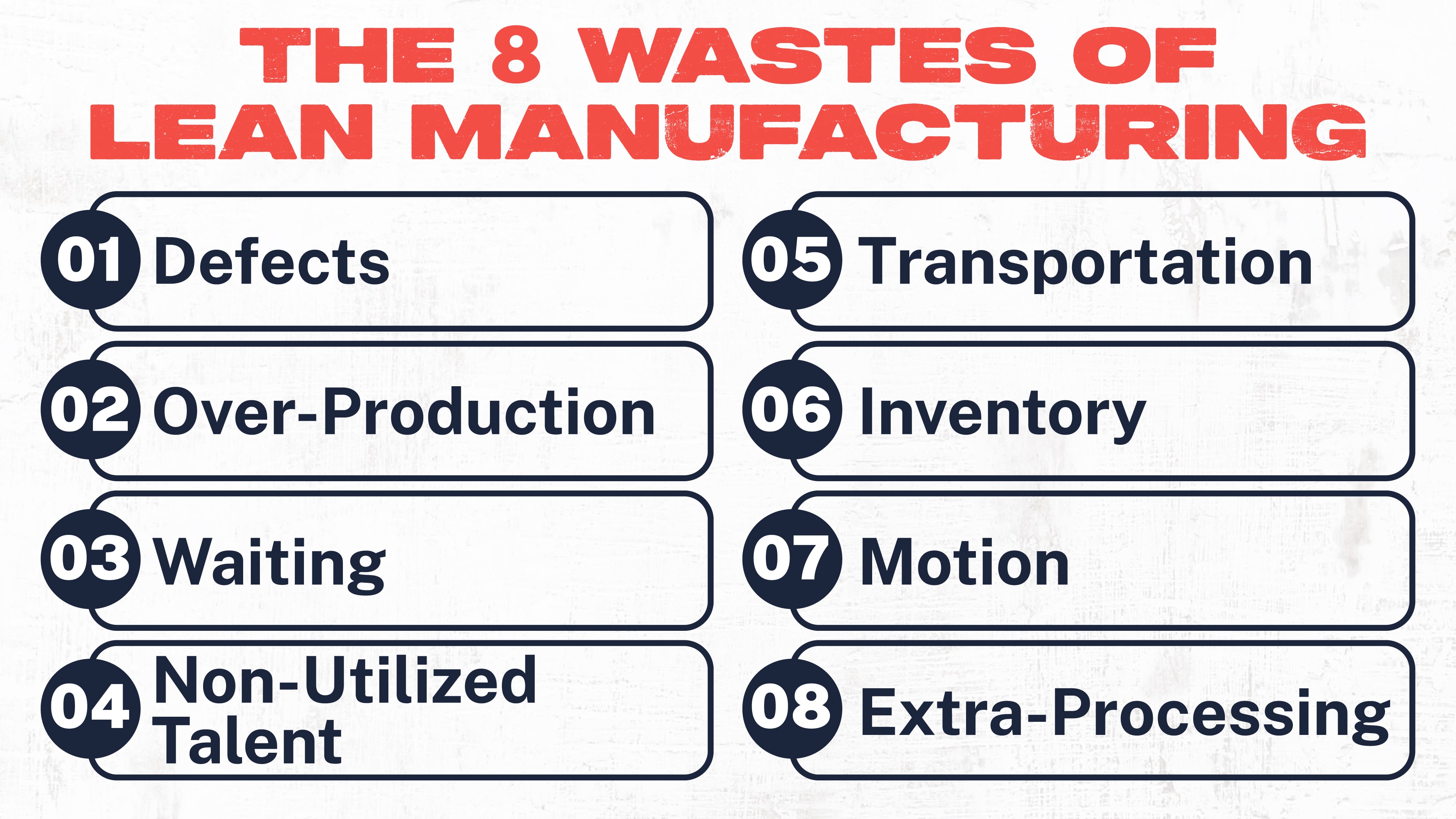
The Japanese identified seven types of waste within a manufacturing system. Over the years, an eighth waste was added: wasted talent. Today, the wastes of lean manufacturing form the acronym "downtime." They are:
- Defects
- Over-Processing
- Waiting
- Non-Utilized Talent
- Transportation
- Inventory
- Motion
- Extra-Processing
Each of these wastes steals productivity and efficiency from a company because they don’t add value for the customer. By eliminating or reducing these wastes, companies can be more efficient with output and quality.
Let’s look at the eight wastes up close.
Defects – The most apparent waste within a manufacturing company is defects or defective products. When a product comes off the line defective or damaged, the company has lost more than the materials used in the process.
Also gone forever are the time and energy used to produce that part, costs associated with handling that part (either through recycling, disposal, or reprocessing), and even wear and tear on the machinery used to produce the part.
Over-Production – Over (or under) production waste occurs when companies make products before they’re needed. Just-in-time manufacturing can resolve this type of waste by only producing products as ordered or just enough to meet demand without stockpiling.
Waiting – The dreaded waiting waste occurs whenever production is stalled. Unplanned downtime, bottlenecks, and poorly organized systems are all causes of waiting for waste.
Non-Utilized Talent – People are the driving force of a company, and their ideas can add incredible value to an organization. When that talent is unrecognized or underappreciated, it is undoubtedly a waste.
Transportation – This type of waste refers to moving materials, parts, and equipment around a facility. Poorly organized logistics systems, as can a poorly designed floor layout, can create transportation waste.
Inventory – Inventory waste occurs when companies stockpile products in preparation for sale. It costs money to store and handle stock, and that money can go to waste when inventory is accumulated without having a buyer ready.
Motion – Motion waste refers to the unnecessary movement of people during production. It creates motion waste whenever a worker needs to stop work to grab materials, move back and forth between workstations, or even reach for an item repeatedly.
Extra-Processing - One of the more unapparent forms of waste comes from extra-processing, or in other words, unnecessary steps in the production process. Companies can save time and resources by eliminating these steps from the system.
Challenges of Lean Manufacturing & Resource Optimization
Lean manufacturing techniques focus on building better systems, eliminating the waste of lean manufacturing, and creating greater value for the customer.
But putting it all together is often challenging for companies for many reasons, one of them being the complexity of the systems within the industry.
It might be a surprising fact that companies that attempt to implement lean manufacturing within their organizations fail at a rate of 70%. Some of that is related to an incompatibility between lean manufacturing and the company itself, while much of it results from poor planning and implementation.

Here are some common challenges organizations encounter when implementing lean manufacturing techniques.
Changing the Culture
Lean Manufacturing requires a change in the way people think about their work. Any new program or initiative within a company requires employees to work together and solve problems. This can be a challenge because humans are creatures of habit and sometimes resist change.
Only with the whole team working together to improve processes continuously will lean manufacturing work. Everyone must be on board.
Upfront Costs
The digital transformation and the creation of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Factory 4.0 have changed the approach required for lean manufacturing. These new technologies can dramatically improve the efficiency and productivity of a company, but they often require a significant upfront investment.
Complexity: The Learning Curve
Lean manufacturing techniques can be challenging to implement because of the complexity of the production process itself. Deep knowledge and understanding of the process are required to make everything work efficiently, and attempting to implement lean manufacturing without this knowledge can do more harm than good.
Tips for Implementing Lean Manufacturing
Overcoming the challenges of implementing any new system requires patience and perseverance. It also requires knowledge of the techniques involved and lean manufacturing waste.
Careful implementation should be step-by-step and involve everyone within an organization. The following tips can help companies build a successful lean manufacturing system.
1. Create Culture Change for Everyone Within the Organization
Changing the way, a team works needs to be focused and consistent. Employees must feel like they’re a part of the initiative and not just at its mercy. Restructuring the company culture with a focus on lean practices at the center is critical to moving everyone forward together and meeting goals.
2. Build the Program to Address Specific Problems and Goals
Going lean can be a huge undertaking. For the best chance at success, companies should focus on creating solutions to problems directly affecting the business or where lean practices will have the most significant impact.
3. Establish an Implementation Plan
Careful planning is the first step to implementing lean manufacturing. A step-by-step process should be established, starting with defining specific goals, setting clear expectations, and pulling in the necessary resources.
4. Training and Communication
Employees deserve the knowledge and skills required to be successful in their roles. Facilitating practical training and development with lean manufacturing at the core will benefit both employees and organizations.
Ongoing communication from team members about the effectiveness of the programs will help them feel like part of a team. And it will provide valuable insights into what’s working and what needs improvement.
Benefits of Effective Lean Manufacturing & Resource Optimization
Identifying and eliminating the waste of lean manufacturing can help organizations be more productive, efficient, and profitable – all while maintaining or improving the value provided to the customer.
Studies show that most manufacturing companies spend less than 5% of their time on value-adding activities, while the other 95% is wasted. With such numbers, it’s easy to see how even a slight improvement could impact organizations.

Below are some of the benefits companies can gain by going lean.
- Improved Quality – Lean manufacturing eliminates waste while maintaining value. This results in fewer products and a guarantee that products will meet or exceed customer requirements.
- Increased Productivity – Reducing waste and streamlining processes will result in greater productivity.
- Reduced Costs – Lower operational costs result from reduced waste, improved efficiency, and a boost in productivity.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction – Producing a more consistent and high-quality product and getting it to the customer faster will inevitably increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased Employee Morale – Lean production techniques often focus on improving the responsibility and involvement of employees. Giving them more control over their work and making them feel like a part of a team will increase morale and retention rates.
- Improved Safety – One objective of lean manufacturing is to make the workplace more organized and Reducing hazards and improving the organization improves the overall safety of workers.
- Greater Sustainability – Reducing waste and lowering energy consumption results in a more sustainable operation.
Strategies for Effective Resource Management & Lean Manufacturing
Removing the waste of lean manufacturing requires understanding the basic principles and techniques.
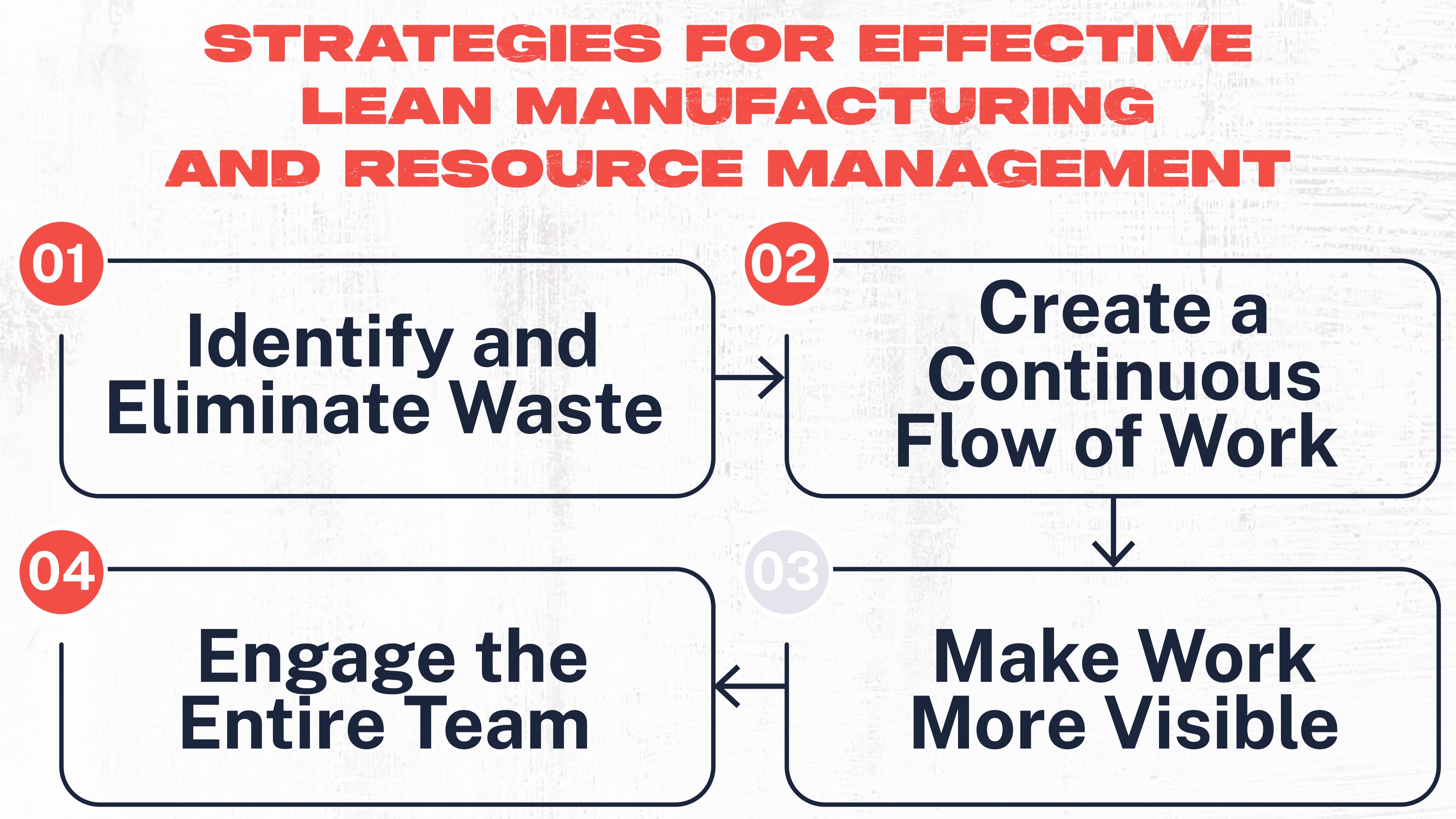
To make the system work the most effectively, companies must:
- Identify and eliminate waste
- Create a continuous flow of work
- Make work more visible
- Engage the entire team
These are the basic principles required to build a successful lean manufacturing system. Some tools and techniques can help organizations achieve each of these goals. These tools aim to make work more efficient and team members more productive.
Improving Visibility
One feature of lean manufacturing is improved visibility into operations – from start to finish. Without the ability to see the details of production and operations, organizations lack the tools required to make improvements.
Visual management can improve every level of operations within an organization, from production to logistics and beyond. It can help track and optimize inventory levels. It can identify critical bottlenecks. And it can improve communication between employees, helping to communicate goals and expectations and building a sense of teamwork.
Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping is one of the most effective tools for increasing visibility into operations. This technique allows companies to identify the steps in producing a product or service.
With a better understanding of those steps, organizations can analyze each component to determine if it’s a value-adding step or if it is creating unnecessary waste. What results in a better ability to identify problems and make improvements?
Applying the 5S Methodology for Workplace Organization & Efficiency
Another effective tool used by lean manufacturing is the 5S methodology. The Japanese developed it as part of their revolutionary lean manufacturing system, but it likely has roots far back. 5S helps to improve workplace organization, efficiency, and safety.

The 5S methodology is adapted from five Japanese words:
- Seiri (Tidiness)
- Seiton (Orderliness)
- Seiso (Cleanliness)
- Seiketsu (Standardization)
- Shitsuke (Discipline)
These five terms explain how manufacturing companies can train employees to take ownership of their workspace. They also show the benefit of keeping a workplace clean and organized and improving productivity, efficiency, and safety.
The Five Steps of 5S
Sort: Identify and remove unnecessary items from the workspace to reduce clutter.
Straighten: Arrange the remaining items most logically and efficiently for the worker.
Shine: Keep the workplace clean and free from clutter while maintaining organization.
Standardize: Create and implement standards to help workers keep the workplace clean and organized.
Sustain: Train employees to implement the 5S principles and follow up to build a culture of continuous improvement.
Implementing and following these five steps will result in a safer and more efficient workplace. In turn, employees will be better able to do their jobs without interruption, less likely to make costly mistakes and have a cleaner, safer workplace.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Production & Inventory
The lean manufacturing tool we will discuss is one of the most effective: Just-in-Time manufacturing. This technique helps to identify and remove two of the costliest wastes of lean manufacturing, over-production and excess inventory.
Just-in-Time manufacturing and inventory management aim to reduce waste by receiving and producing goods as close as possible to when needed. Instead of spending time and resources creating and storing goods in expectation, production meets demand head-on.
Just-in-Time manufacturing has many benefits for companies, including a reduction in production and inventory storage costs. But it can also present unique challenges, especially if forecasting methods fall short.
The last thing a company wants is to be unable to fulfill a customer’s order on time. So, JIT must be done with careful planning.
%20Production%20%26%20Inventory.jpg?width=4000&height=2250&name=Just-in-Time%20(JIT)%20Production%20%26%20Inventory.jpg)
The Pros of JIT
- Minimizes on-site materials and inventory
- Reduces production and warehousing costs
- Reduces or eliminates wasted inventory (especially in the case of perishable goods or materials)
- Reduced time for production runs
The Cons of JIT
- Susceptibility to disruptions in the supply chain
- Potential for stalled production because of a delay in materials
- Inability to meet large or unexpected orders on time
- Potential to lose customers if not implemented with accurate forecasting
The Importance in Employee Training and Development
As mentioned, employees are key to effectively making any new initiative work. With the entire team's involvement, it will be easier to meet goals and expectations. This requires team members to be invested in the initiative's success and the organization itself.
Just-in-Time manufacturing requires a very delicate balance between supply and demand. Employees must have the proper training, knowledge, and skills to get it right. Organizations have a responsibility to provide training and development opportunities for every employee.
With that key component, they can implement a system that will likely succeed. And they are likely to have a higher turnover rate because an untrained employee is less likely to succeed in their job and less likely to maintain a positive outlook on their organization.
Tools & Techniques to Support Lean Manufacturing
We’ve already covered some of the practical tools and techniques of lean manufacturing, including identifying lean manufacturing wastes, JIT manufacturing, and the 5S methodology.
There are many tools that companies can use to build a successful lean manufacturing system, and choosing the right ones depends on the specific needs and requirements of the organization. Let’s look at some more lean manufacturing techniques.
Kaizen
Kaizen is a philosophy that centers on reaching for continuous improvement. It can be applied to every aspect of a business, from design to production and even customer service. Consistently implementing Kaizen means always looking for ways to get better.
Kanban
Kanban is a workflow management method that focuses on helping teams visualize work and streamline production processes. Companies can be more efficient and productive by focusing on optimizing workflow and limiting the amount of work-in-progress to what is most needed and beneficial.
Standardized Work
Standardized work is a lean manufacturing practice that helps employees define the best way to perform a task. It is a systematic approach that identifies and documents every step involved in a job and the time and resources required to complete it.
By giving employees a structured formula, companies can guarantee that work is performed the same way and to the highest standard every time. This eliminates variations and guesswork, which results in greater efficiency and safety and a higher quality product.
Total Productive Maintenance
Maintenance is a necessary evil in manufacturing. Production is stalled when a piece of equipment goes down, either expectedly or unexpectedly. Total Productive Maintenance is a lean manufacturing method that aims to improve the overall effectiveness of production equipment and make maintenance activities work to the best benefit of the organization.
Final Thoughts
Identifying and removing the waste of lean manufacturing can help companies be more efficient, productive, profitable, and competitive. Using various tools and techniques, such as just-in-time manufacturing, Kaizen, standardized work, and more, helps companies remain focused on continuous improvement.
Doing more with less and understanding that organizations can always be better is at the heart of lean manufacturing. And the principles and methodology of these techniques have become a standard for manufacturing companies because of their benefit and effectiveness.
However, implementing these systems successfully requires careful planning. There are probably better approaches than jumping in headfirst. Instead, companies should take a big-picture approach and identify areas where lean manufacturing would make the most significant impact.
On top of that, manufacturing companies must adapt lean techniques to the new technological age. Lean manufacturing today looks very different than it did just a decade ago. Digital tools, automation, software, AI, and machine learning are giving manufacturing companies a greater variety of strategies to improve the benefits of lean manufacturing.
Putting it all together and figuring out how to eliminate waste without affecting the quality of the output is the key.
Topic(s):
Frontline Digital Transformation
Improve Operations with Dozuki
Get a demo to learn more about how Dozuki is helping operational leaders transform their frontline workforce to achieve success.
Related Posts
View All Posts
Continuous Improvement
Streamlining Production: How Lean Manufacturing Can Revolutionize Your Business
23 min read
Manufacturing is a delicate process. So many moving parts must come together just right if the aim is to produce goods of the highest quality in the most cost-effective way...
Continue Reading
Continuous Improvement
Lean Manufacturing Lessons From Wikipedia
5 min read
When Jimmy Wales, founder of Wikipedia, was interviewed on NPR’s “How I Built This,” he revealed a valuable insight — sharing and improving knowledge is hard work. The...
Continue Reading
Industry News
The Manufacturing Skills Gap is an Opportunity
4 min read
There is a pending manufacturing skills gap impacting the United States workforce. Millions of positions are expected to go unfilled in the coming years, with reports...
Continue Reading