Best Practices to Maximize Production Capacity in Manufacturing | 2023

According to the numbers, manufacturing makes up around 12% of the U.S. GDP and provides jobs for 12.984 million Americans, or about 9.6% of all U.S. workers. In other words, manufacturing is a big business.
Table of Contents
1. Lean Manufacturing Principles
2. Lean Manufacturing & Production Capacity
3. Automation & Robotics Integration
4. The Role of Automation in Production Capacity
5. Optimizing Equipment & Machinery
6. Employee Training & Skill Development
7. Effective Inventory Management
8. Quality Control & Assurance
9. Bottleneck Identification & Mitigation
10. Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
11. Real-Time Monitoring & Data Analytics
12. Collaboration & Communication

For manufacturing companies, there is incredible competition in the market. This competition makes it incredibly important for organizations to maximize their production capacity.
One key component to success in manufacturing is figuring out how to do more with less – without sacrificing quality or safety.
Effective production planning and scheduling is one way manufacturers can optimize resource utilization and minimize downtime.
Production planning considers market demand and sales forecasts to ensure resources are allocated efficiently. It strives to make sure that companies are producing what is needed when it is required.
Production scheduling uses the information generated by production planning to create specific production schedules, accounting for all the details needed to pull it off effectively. That includes things like the availability of resources, labor, and machinery.
Production planning and scheduling work together to help manufacturers determine what to produce when, and how much to produce. It is a critical function for manufacturers, helping them meet customer demand, minimize costs, and optimize resource utilization.
This article will discuss some best practices manufacturers can use to maximize production capacity and make the most of every operational dollar.
Lean Manufacturing Principles
We can’t discuss production capacity without mentioning lean manufacturing. Lean manufacturing is a method of production that emphasizes waste reduction to maintain the goal of continuous improvement.
Put forth as a concept by the Toyota Motor Corporation in the mid-1950s; lean manufacturing includes five main principles that manufacturers should follow to help them build a lean culture.
They include:
- Value
- Value Stream
- Flow
- Pull
- Perfection
Each of these principles represents a cog in the lean manufacturing machine. It starts with identifying the value of each step in the production process. In other words, what kind of value does each step add to the final product?
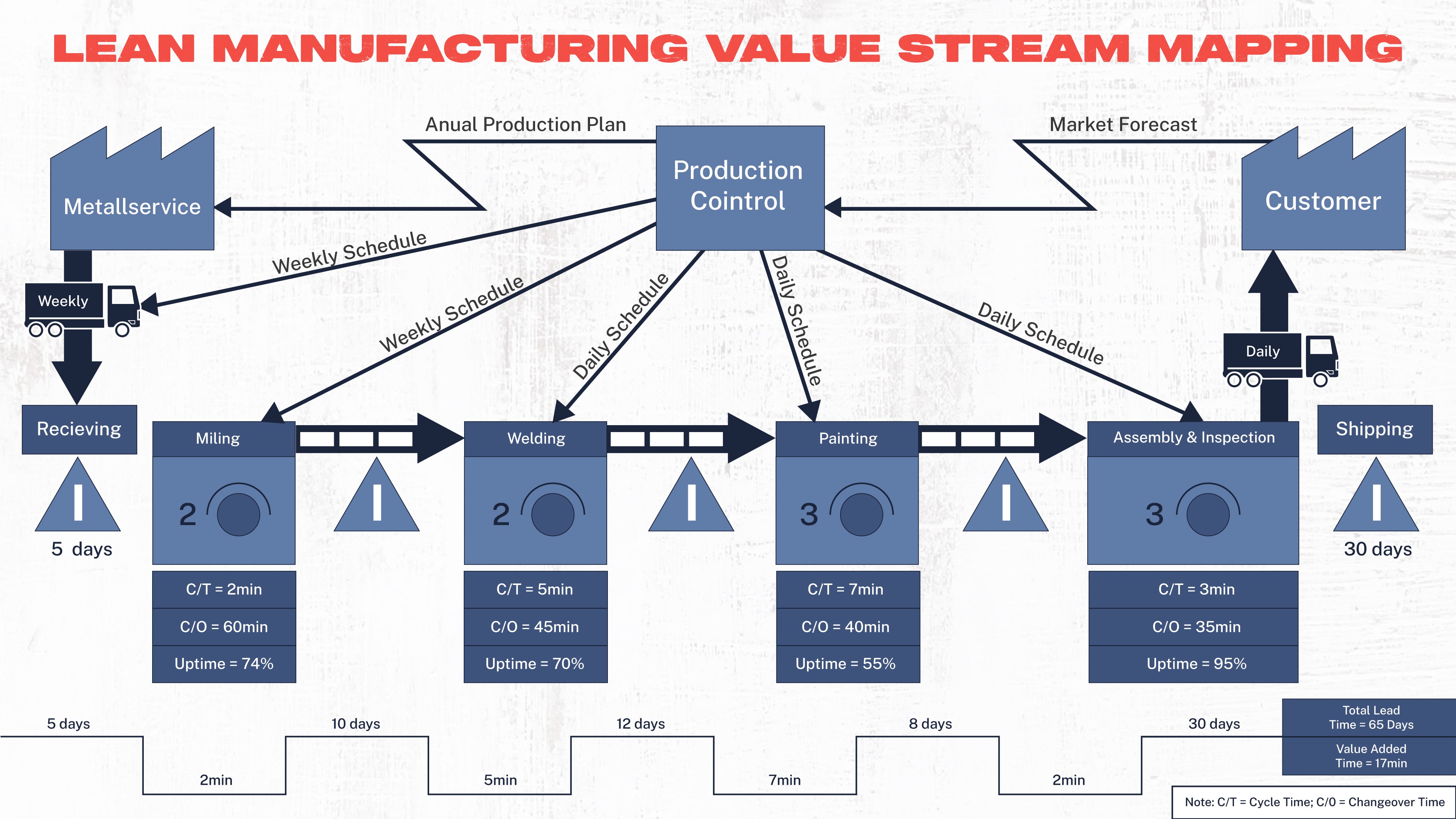
Next, manufacturers should map the value stream. This requires visualizing every step in the production process and pinpointing which non-value-adding steps can be eliminated without affecting the quality of the final product.
The following lean manufacturing principle involves ensuring the production process still flows efficiently. This is critical, especially if potentially wasteful steps have been removed.
Secondary to flow is the principle of flow, which means aligning production with consumer demand. Ensuring production matches demand helps to eliminate waste and maximize profits.
Lastly, lean manufacturing centers around the principle of perfection. The term “continuous improvement” helps manufacturers remember that they should strive to improve.
Constantly considering perfection as a goal will motivate team members to look for areas where improvements can be made.
Lean Manufacturing & Production Capacity
This article is focused on how to boost production capacity. Manufacturers need to realize that incorporating lean manufacturing principles into their culture is one of the best ways to do that.
By following the five principles and striving for continuous improvement, manufacturers can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
And they can make the most of their production process, meaning higher output at a lower price.
Consider that manufacturing shutdowns can eat up between 1% -10% of production time, whether planned or unplanned.

Lean manufacturing and production planning can help manufacturers avoid this type of waste, saving billions of dollars.
Automation & Robotics Integration
Lean manufacturing has been a common practice in manufacturing plants for almost a century. However, the techniques used in the 1950s look very different from those in play today.
Robotics and automation are the new way to go lean. And the reason manufacturers are turning to automation to eliminate waste makes perfect sense.
Automation is how manufacturers can use technology to perform tasks that would otherwise require a human worker to accomplish.
While there has been some fear surrounding the implementation of robotics in the workplace, the truth is that automation doesn’t necessarily eliminate jobs – it just reallocates workers to a more productive role.
The Role of Automation in Production Capacity
The global automation market is expected to reach more than $130 billion by 2026.
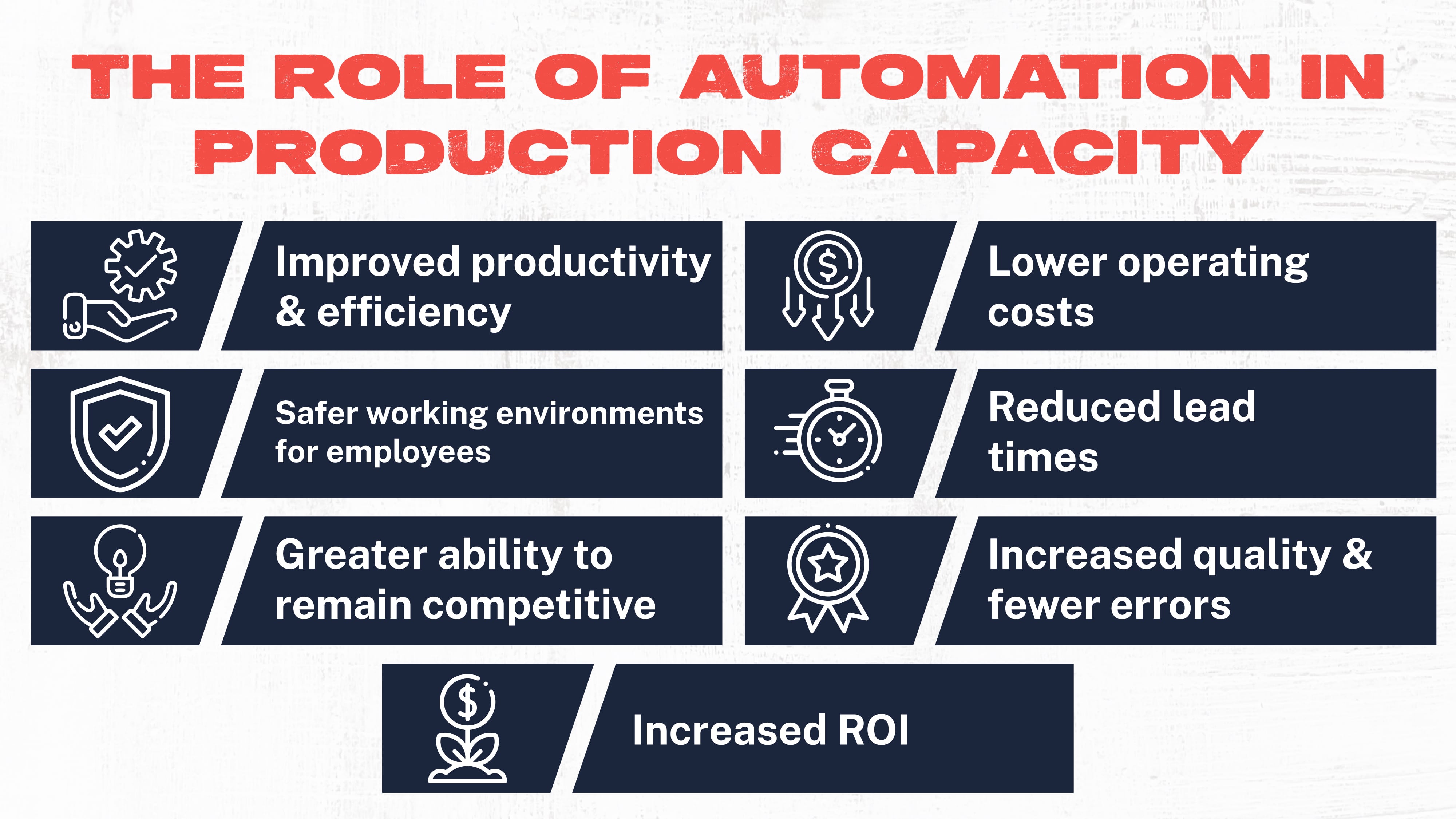
Manufacturers who implement innovative technology and robotics in their operations stand to gain a long list of benefits, including:
- Improved productivity and efficiency
- Lower operating costs
- Safer working environments for employees
- Reduced lead times
- Greater ability to remain competitive
- Increased quality and fewer errors
- Increased ROI
Optimizing Equipment & Machinery
Manufacturing companies would not get very far without equipment and machinery. Manufacturers looking to boost their production capacity should take a long, hard look at the machinery they are using to get the job done.
Equipment maintenance includes the inspection, lubrication, and repair of equipment and machinery.
And it uses a combination of preventative, predictive, and corrective maintenance techniques to ensure that machinery is operating in peak condition when needed the most.
Effective equipment maintenance is essential for running a smooth operation. Ready for some big numbers? According to Aberdeen Research, unplanned downtime can cost a manufacturer as much as $260,000 – in a single hour.
Effective maintenance practices are one way that organizations can limit downtime and its high price tag.
Maintenance also helps to improve the quality of the products that reach customers. It keeps operational and repair costs low. And it keeps customers happy by ensuring production is running at peak capacity.
Employee Training & Skill Development
Another way that manufacturers can increase their production capacity is by paying particular attention to the people tasked with the production itself – the employees.
Employee training and development is more than beneficial for manufacturers; it’s vital for the success of any manufacturing organization.
Poorly trained employees become an incredible liability. They are more likely to make costly errors, promote unsafe working conditions, and produce a lower-quality product.
They are also more likely to leave an organization if their lack of training and development is the company's fault. Employees want to do a good job. They want to succeed. And they want to advance in their role.
An engaged and motivated workforce benefits any company. When it comes to the manufacturing industry, having a highly skilled and well-trained team at the helm means a greater ability to remain productive, improved efficiency, and higher-quality output. Plus – happier employees.
Employee training and development is simply a wise investment.
After all, manufacturers rely on their workers to run expensive and potentially dangerous equipment.
Providing the proper training, cross-training, and real-time experience ensures workers can do their jobs successfully and safely.
Effective Inventory Management
Maximizing production capacity means higher output. But it doesn’t necessarily have to mean more inventory. Effective inventory management and production scheduling go together.
Or at least, they should. It makes no sense to boost production without also considering the inventory involved.
Inventory optimization involves managing inventory levels to benefit the organization and the customer.
To minimize costs and maximize profits, manufacturers need to balance their inventory levels with market demand and then consider production planning and scheduling into the equation.
There are numerous techniques that manufacturers can use to optimize their inventory management.
Choosing the right one will require careful consideration of the needs of the business.
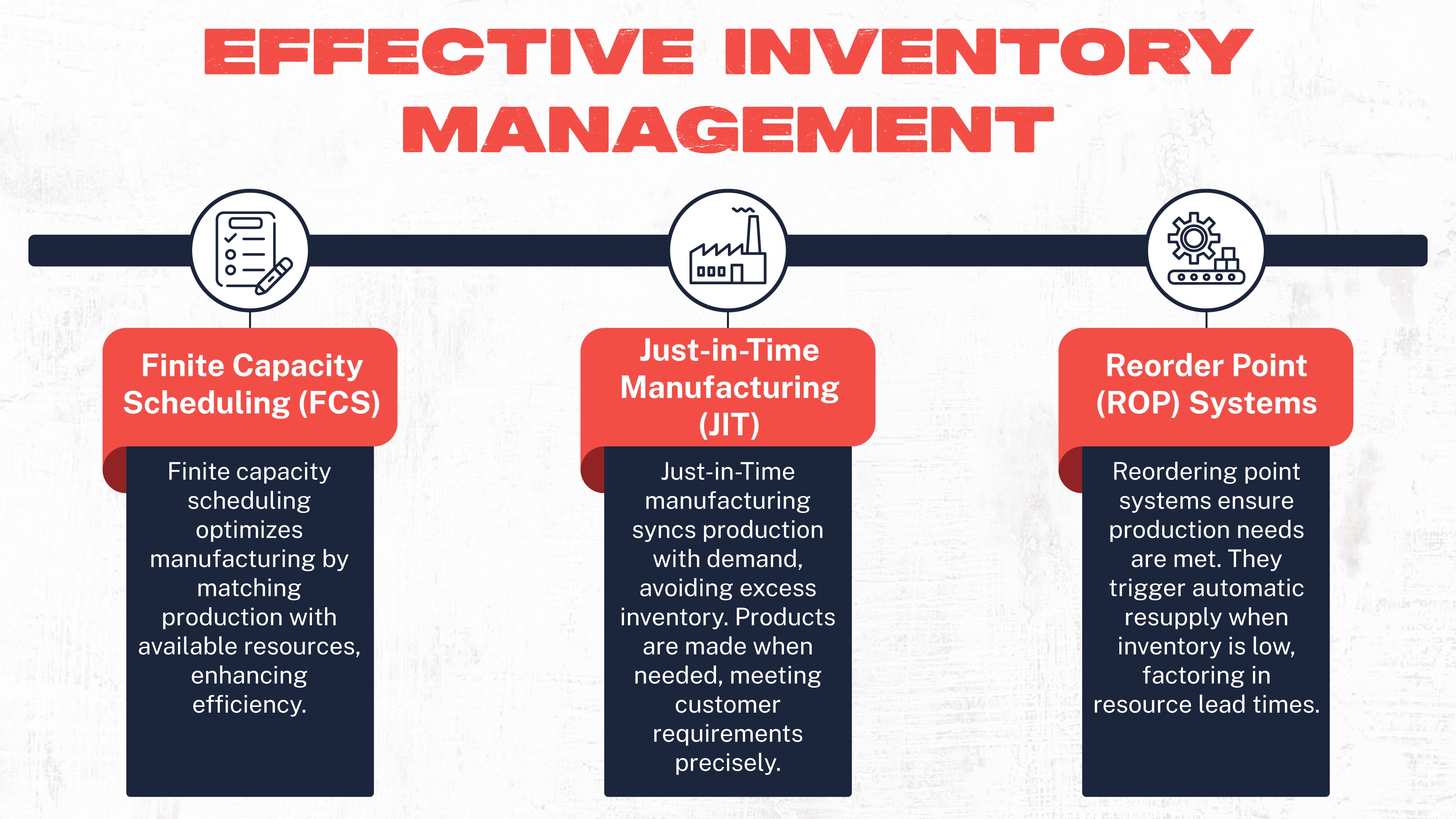
Finite Capacity Scheduling (FCS)
Finite capacity scheduling is one way manufacturers can optimize resource utilization and boost production capacity.
This inventory management technique focuses on matching production with resource availability. Understanding what materials are available at a specific time can help optimize production scheduling.
Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT)
Just-in-Time manufacturing helps to effectively manage inventory levels by matching production with demand.
By producing goods just before they are needed or as a customer needs them, companies avoid building excess products that are not yet required. And manufacturers can offer the customer exactly what they need when needed.
Reorder Point (ROP) Systems
Reordering point systems are a way for manufacturers to ensure they have what they need to meet production goals.
By using systems that allow for specific inventory level triggers, supplies, and resources are automatically ordered when stock runs low. These systems consider the specifics of the inventory management process, including how long it will take to get the needed resources.
Quality Control & Assurance
When it comes to manufacturing, quality control, and assurance should be top of mind in every single conversation. That includes production capacity, planning, and scheduling.
It does no good to boost production if the result comes with a lower-quality product. And the truth is that a focus on quality can help manufacturers hit those production goals.
Quality assurance (QA) is a preventative approach to quality, meaning manufacturers work to ensure products meet quality standards before they ever reach consumers.
Quality control (QC) is a reactive approach to quality. It focuses on identifying defects and correcting the factors that caused them to occur in the first place.
Both play an essential role in a manufacturer's ability to provide a high-quality product to consumers without wasting valuable resources, and dollars, in the process. And both offer an effective avenue for manufacturers to boost production capacity.
Here’s how it works:
QA seeks to eliminate the possibility of defects occurring.
QC seeks to identify and correct processes that result in defective products as soon as possible—both free up time and resources for higher-quality production, saving manufacturers money and customers.
Bottleneck Identification & Mitigation
If there’s anything more detrimental to a manufacturer’s ability to maintain production capacity, it’s the dreaded bottleneck. A bottleneck occurs whenever and wherever work slows or stops for any reason. For manufacturers, maintaining a consistent production schedule is vital.
Bottlenecks often cause a snowball effect, meaning when work stops somewhere on the line, it also stops at every point down the line.
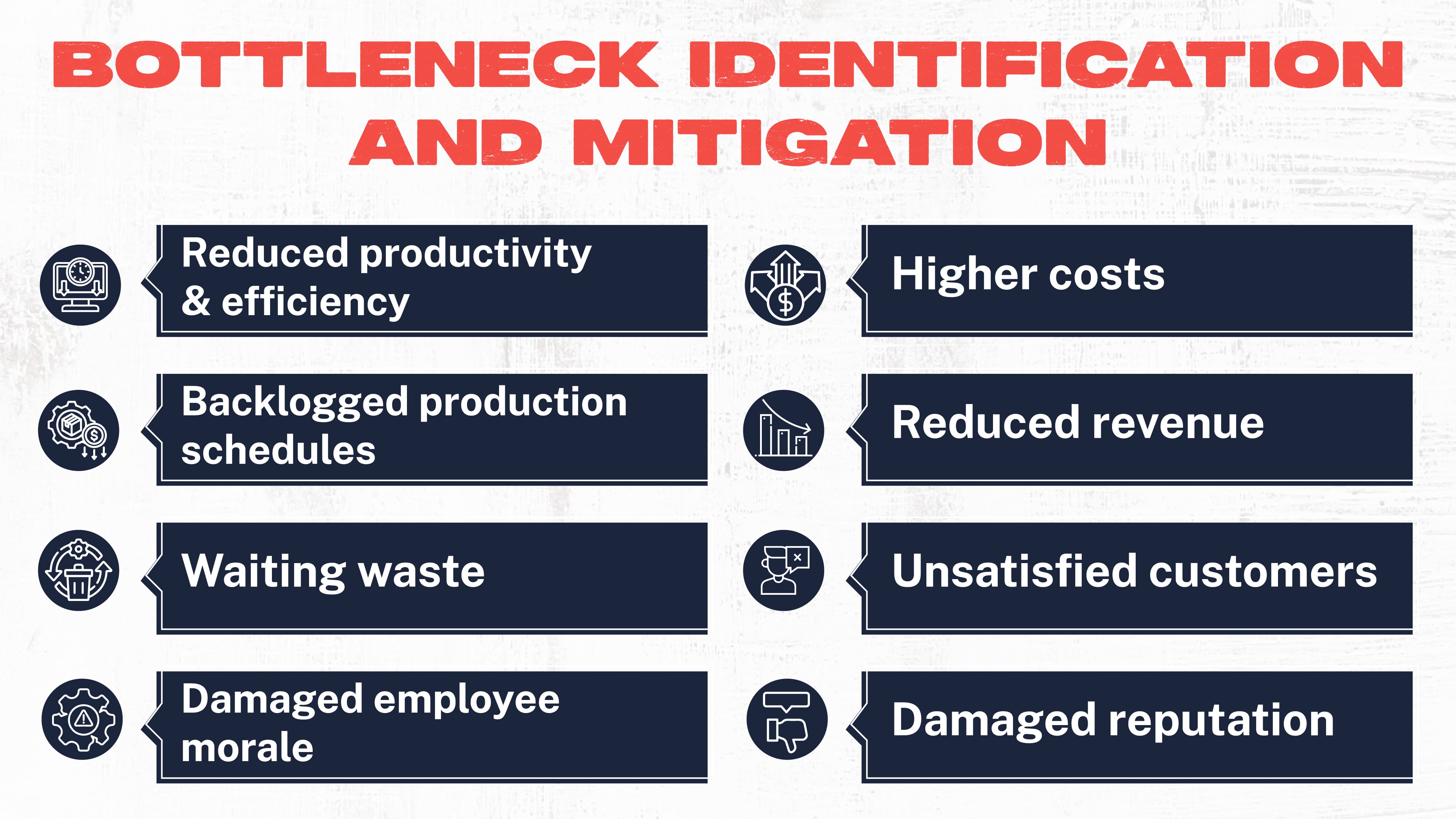
Some other effects of bottlenecks include:
- Reduced productivity and efficiency
- Backlogged production schedules
- Waiting for waste
- Damaged employee morale
- Higher costs
- Reduced revenue
- Unsatisfied customers
- Damaged reputation
Like most things in manufacturing, the negative effects of bottlenecks extend to virtually every corner of the business.
That’s why manufacturers must work proactively to mitigate and eliminate bottlenecks in their production processes. Here are a few tips on how to do it:
Process Mapping
Process mapping is an effective way to measure the success of a production process and a great way to identify shortfalls. Process mapping should include all the relevant details of a particular process, including:
- Specific workers tasked with each step
- Resources and factors that contribute to a successful process
- How each step in the process leads into the next
- The goal or outcome
Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a tool that manufacturers can use to drill down to the actual first cause of any problem. When it comes to bottlenecks, this can be complicated. That’s because, as mentioned before, bottlenecks often cause a snowball effect.
Remedying a problem at the end of the production line won’t necessarily eliminate the bottleneck. Root cause analysis helps link causative effects until the original cause is identified.
Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
Sustainable manufacturing practices are more critical than ever before. The reason is two-fold.
First, consumers expect and appreciate companies actively working to reduce their environmental impact.
And secondly, wasteful practices hurt a company’s bottom line.
When it comes to finding a link between energy efficiency and production capacity, it might not be as apparent as some of the other practices on our list. But the relationship is undoubtedly there.
To understand more, let’s look at the benefits of sustainable manufacturing.
- Reduced environmental impact
- Increased efficiency
- Improved bottom line
- More loyal customer base
- Improved reputation
- Lowered costs related to fines and regulations
The link between an increased ability to maintain efficiency in operations and a better ability to boost production capacity should be apparent.
Efficiency means using time, resources, machinery, and labor the most effectively. Being more efficient makes it possible for manufacturers also to be more productive. And there you have it.
There are numerous ways that manufacturers can achieve the goal of sustainable manufacturing, including:
Reducing Waste – Reducing environmental impact starts with reducing waste, a practice directly related to lean manufacturing principles. It only benefits manufacturers to reduce waste, both physical and non-physical.
Using Renewable Energy – One of the most effective ways to reduce an organization’s environmental footprint is to seek renewable energy sources. In 2020, the industrial sector contributed 24% of greenhouse emissions in the United States. Using renewable energy sources is one of the most effective ways to reduce this impact.

Using Resources Efficiently – A great deal of waste produced within manufacturing because of the misuse and mismanagement of resources. Careful production planning and scheduling can help manufacturers use resources more efficiently.
Real-Time Monitoring & Data Analytics
Manufacturers can increase their production capacity in several ways. One of those ways is by using real-time monitoring and data analytics, which have recently undergone a massive transformation thanks to technology.
Real-time data analytics can provide businesses with immediate insights into the efficiency and success of their operations, from a big-picture perspective down to an individual step within a process.
As they say, knowledge is power. And when it comes to manufacturing and business in general, real-time knowledge can help companies make smarter decisions.
Like many of the other practices on this list, real-time monitoring and data analytics provide manufacturers with a host of benefits, including:
- Increase efficiency
- Improved customer service
- Increased profitability
Technology and analytics work together in today’s manufacturing landscape. By implementing the right technology in the right places, organizations can clearly understand operations at any given moment. And they can use that data to forecast a future of possibilities and outcomes. Welcome to the end of manufacturing.
Collaboration & Communication
While many practices on our list of ways manufacturers can boost production capacity are specific and targeted to a particular area, this next one is far-reaching. Collaboration and communication might seem vague to some, but its impact is anything but.
The Cambridge Dictionary defines collaboration as “the situation of two or more people working together to create or achieve the same thing.”
Collaboration can help organizations make better decisions, be more productive, and boost problem-solving and creativity. Thinking together instead of individually means a better chance of success, no matter the situation.
Working Better Together
Collaboration is an essential skill in virtually any workplace. And for collaboration to be successful, employees must communicate effectively.
Communication within an organization, whether between departments, employees and supervisors, or between the CEO and the rest of the company, is essential. Valuing communication and providing employees with the right pathways to share information openly is vital.
Without well-established channels, employees may not know how to communicate effectively. Or they may lack the support and confidence to share ideas.
Organizations can combat this by providing employees the time and space to brainstorm, communicate, and collaborate.
And as for production capacity, manufacturers should provide workers with the right tools to effectively manage communications in real-time.
Supply Chain Optimization
Thanks to the pandemic effect, even the average consumer has become an expert on the supply chain. The global health crisis threw the global supply chain network into upheaval.
Shutdowns and shortages left many businesses without the materials or products they needed, and increased transportation costs and delays made it harder to get the supplies that were still available.
This spiral effect took a lot of people by surprise. But the lesson here is this: everything is connected, and when one cog in the machine stops moving – the entire machine comes to a halt. And it highlighted the importance of supply chain optimization to safeguard against future catastrophes and, yes, boost production capacity.
How & Why to Achieve Supply Chain Optimization
Effective supply chain optimization requires a commitment from all stakeholders in the supply chain. And it needs visibility into each step of the process.
This visibility can help manufacturers spot potential weaknesses in the supply chain and put them in a better position to prevent links in the chain from falling apart.
Supply chain optimization is one of the most effective ways for a manufacturing organization to keep costs low. It also helps boost efficiency and, therefore productivity.
And it ensures that customers remain satisfied with a consistent, high-quality product – regardless of outside factors that threaten the entire structure.
Final Thoughts
There you have it – a list of some best practices manufacturers can use to boost their production capacity. It’s important to remember that the best practices that are most effective for a particular manufacturer will differ and will depend significantly on the business's specific needs.
However, every item on this list can have the capability to help manufacturers improve their overall efficiency, reduce operational costs, and boost productivity and production. And, of course, the result is improved customer satisfaction and a more prosperous and sustainable organization.
So, what can organizations take from this list specifically? Simply this: manufacturing is a big operation that requires many moving parts. Often, each of those moving parts is connected. Focusing on the right areas can influence a company's ability to remain productive and be more productive in the long term.

Written by Scott Ginsberg
Related Posts
The New Playbook for Operational Learning and Development
How Dozuki empowers training leaders to close skills gaps, accelerate onboarding, and enforce standard work at scale. Training is No Longer a Department, It's a System ...
Continue Reading →Rethinking MES in the Era of the Connected Workforce
Most Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) were built to rigidly enforce processes, not to empower people or evolve how work gets done. MES platforms excel at orchestrating...
Continue Reading →Dozuki Announces Record Breaking 2025
Dozuki in 2025: Cementing Global Leadership in the Connected Worker Category Dozuki, the pioneer of the Connected Worker Platform since 2011, today announced its most...
Continue Reading →