How To Reduce Defects in Manufacturing in 2022

Product defects are a pain at any manufacturing company. When all the time, energy, and money that is spent to produce a product is wasted due to defects in the final outcome, it can have a huge effect on the company.
This effect can be widespread, from an increase in the cost per unit of an item to decreased customer satisfaction, and even a negative effect on the company's overall reputation and success.
The negative effects of product defects:
-
Financial losses, a lowered bottom line, and a decreased ROI
-
Lowered productivity due to lost manufacturing time and a lowered efficiency
-
Extra costs involved with fixing, discarding, or repurposing damaged or defective products
-
Extra costs resulting from addition in payroll needed to rectify issues
-
Decreases customer satisfaction and loyalty, and an increased need to handle customer complaints, up to and including possible litigation
-
A negative effect on the overall reputation of a company
A manufacturer relies on the success of its products, so it becomes very important to seek out, identify, and rectify, any issues that would result or have already resulted in product defects.
There are proactive steps a company should take to reduce manufacturing defects, or even prevent them before they occur.
In this article, we will discuss the definition and types of product defects that are common in the manufacturing industry. We will highlight the potential causes of these defects and list some tips and strategies for reducing defects in manufacturing.
Assessing the Common Defects in Manufacturing
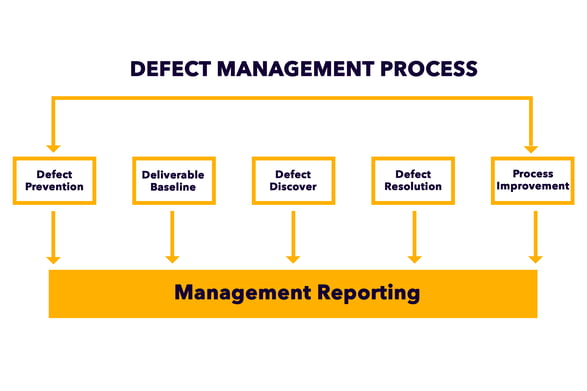 The biggest tool companies have at their disposal to reduce manufacturing defects is the overarching idea of manufacturing area optimization.
The biggest tool companies have at their disposal to reduce manufacturing defects is the overarching idea of manufacturing area optimization.
But what does that truly mean?
Optimization refers to utilizing every method, tool, and process to create the best environment and get the best result possible.
This includes identifying opportunities for improvements in every step of each process and implementing consistent and long-standing changes in standards and actions.
The goal is to produce the highest output possible using the lowest number of resources while maintaining the highest achievable quality. So, how do companies begin this process?
-
Evaluate the quality and standards in each supplier, including the raw materials needed to create each product and every step in the process which is outsourced.
-
Evaluate the process and success of each piece of machinery, including each action the machine completes during the manufacturing of a product.
-
Consider the actions, training, and performance of each employee, supervisor, and team tasked with any step in the manufacturing process.
-
Uphold high-quality control standards and procedures to ensure compliance and focus company goals toward excellence.
-
Stick to a regular and dedicated maintenance schedule to prevent defects as a result of machine breakdown or failure.
-
Utilize technology to automate steps that have a high incidence of error and eliminate complex, lengthy, or repetitive steps in every process.
-
Consider the effectiveness of control loops and identify areas where they may overlap or be unproductive.
Utilizing manufacturing area optimization can help reduce manufacturing defects by identifying steps in the process that may result, or have already resulted, in product defects.
Figuring out exactly where the problem lies is the first step to creating a plan for correcting the issue.
So let's list the possible and common defects that manufacturers encounter in the industry as a whole:
-
Design Defects – Unintentional defects in the design specifications of a product
-
Raw Material Defects – Defects present in the raw materials used in the production process
-
Visual Defects – Defects in the appearance of any part of a finished product, including errors that could cause potential injury, like sharp or jagged edges
-
Functional Defects – Defects in the intended function or purpose of a product
-
Assembly Defects – Defects in the way products are assembled
-
Construction Defects – Defects in the materials used to construct a product, like screws, bolts, or fasteners
-
Electrical Defects – Defects in the wiring or electrical components of a product
-
Harmful Chemical Defects – Defects related to the unintentional harm caused by chemicals used in the production process
-
Printing or Packaging Defects – Defects related to the printing or packaging of a product
-
Marketing or Sales Defects – Defects in the marketing, sales, or distribution strategy of a product
What Are The Major Causes of Manufacturing Defects?
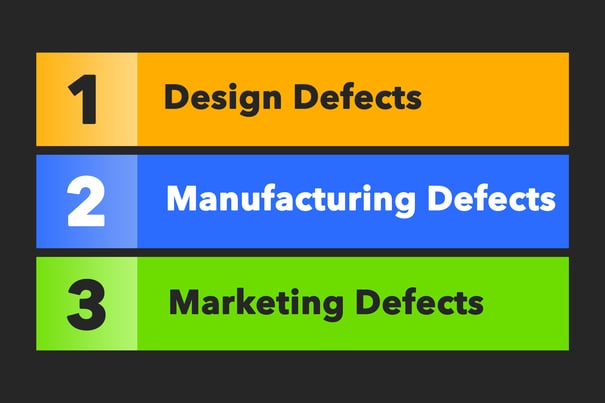
When determining the causes of manufacturing defects, it’s necessary to link a direct or indirect cause to the resulting defect. Defects can be sorted into three main categories: Design defects, manufacturing defects, and marketing defects.
Design Defects
Some defects are the result of faulty designs and can be considered planned defects. While this doesn't automatically classify them as intentional actions, some designers take calculated risks when crafting design specifications.
This would be considered an intentional defect. An example would be a design that incorporates a potentially hazardous chemical, a poor-quality material, or a process with a high possibility of failure. A design flaw will result in a defect that affects every individual product in the line uniformly.
How to Avoid Design Defects
Utilize expert advice from the design team, and consider every possible outcome of a design before beginning production. Consider the use of appropriate materials in every step of the process.
Take advantage of data-driven technology and model-based outcomes to measure the probability of defects down the line. Use proper testing for every step of the design process, up to and including the finished product.
Manufacturing defects
Manufacturing defects are those that occur during the manufacturing process itself and are typically unplanned and unintentional.
These defects most commonly result from a flaw in the process resulting from machine failure or human error.
These types of errors are more likely to result in sporadic defects, and not spread across the entire product line.
Examples of manufacturing defects include visual defects, construction or assembly defects, and functional defects.
How To Reduce Manufacturing Defects
Use a step-by-step investigative process to examine each cog in the gear of the manufacturing process. This includes the machinery, tools, and equipment used in the process.
Ensure proper and targeted training of employees tasked with operating complex machinery to reduce the occurrence of human errors. Utilize ERP systems to streamline processes, automate tasks with a high percentage of error, and take advantage of technologies like the Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT).
"We used to rely on memory and luck. Now it’s step-by-step clarity."
— Tyler L., Production Operator, General Mills
Marketing Defects
Marketing defects don't necessarily describe a faulty product but relate directly to how a product was marketed to the consumer.
Misleading a consumer on the way a product works, performs, or the inherent safety or potential danger of a product is a huge liability for companies.
How To Avoid Marketing Defects
Properly packaging products include the inclusion of detailed and easy-to-understand instructions for proper and improper use protect companies from possible litigation due to misuse of a product.
Any product that could result in injury, illness, accident, or potential bodily harm or property damage should include appropriate and highly visible warning labels. Failure to do so could result in legal repercussions for a company.
The action taken to correct a product defect will be highly dependent on the cause. There are strategies that companies can take to proactively combat specific defects and safeguard against potential defects as a whole.
What Are the Benefits of Reducing Manufacturing Defects?
 The benefits of reducing manufacturing defects can be measured by increased productivity and efficiency.
The benefits of reducing manufacturing defects can be measured by increased productivity and efficiency.
Any product defect is considered waste, and not just the physical waste of the product and materials themselves. Defects result in an increased need for manpower, to both produce replacement products and repair direct causes of defects.
They result in potential downtime for machinery while repairs or changes are implemented. And they waste resources while handling or disposing of defective products.
So, it’s easy to see why reducing manufacturing defects can have numerous direct benefits for a company. The potential benefits of proactively preventing defects from occurring in the first place include:
-
Increased profits
-
Lowered overhead
-
More efficient management of time and resources
-
Greater customer satisfaction
-
Increase in return business
-
Fewer complaints need to be handled
-
Improved company performance and reputation
With so many direct benefits to be gained from reducing the number of defects during production, manufacturing companies need to embrace the idea of zero defects.
And while a quantifiable amount of zero defects is essentially unattainable, the idea behind zero defects can be known as striving for continuous improvement.
Continuous improvement means a company consistently strives to streamline and improve every process involved in the manufacturing of its products.
There are a few standard practices companies can implement to instill a culture of continuous improvement in their workforce:
-
Use a proactive approach to analyze processes and identify errors that lead to defects as soon as possible. The quicker a defect is detected, the faster the issue can be addressed. This limits the number of defective products produced by recognizing issues immediately.
-
Implement strict quality control procedures during every step of the process.
-
Utilize sophisticated testing and data-driven analysis to anticipate where issues may arise.
-
Integrate the processes of every step of production utilizing technology and automation.
-
Hire an expert consulting company to detail a moment-by-moment analysis of the manufacturing process, and use their advice to target areas for improvement.
-
Train, retrain, and target train employees to garner better results due to increased knowledge of processes. Ensure employees know how to identify potential issues that could create defects and lead to waste.
-
Track and monitor employee performance as it relates to errors in production.
-
Motivate employees and team members to constantly strive for improvement.
Effects of Excess Manufacturing Defects
Piling up defects results in a hard hit to the overall productivity of a company.
So, what happens when a single defect goes unnoticed?
For manufacturing companies, when a defect is not recognized and rectified quickly, the repercussions can be catastrophic. This can be both in terms of the financial cost, and the cost to the reputation of the company as a whole.
This negative effect is evident when the defect is detected before the product leaves the plant but is even more damaging if the defective products make it to the consumer.
Consumer complaints and product recalls can permanently damage a company’s reputation, especially in the new age of social media. It only takes seconds for news of a product defect to circle the globe.
Let’s consider some of the biggest recent product recalls, and the effect on the reputation of those companies. After looking at these examples, it's easy to see why reducing manufacturing defects is vital to the productivity, reputation, and overall success of a company.
Boeing 737 Max
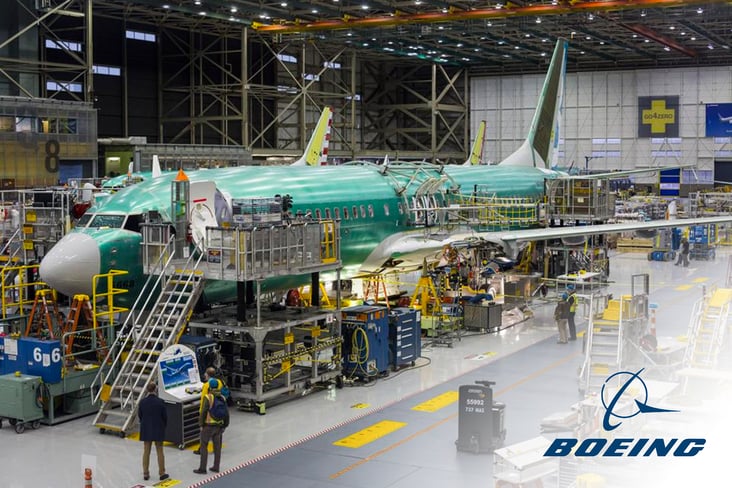

In terms of the negative effect of product defects, nothing could be greater than a loss of human life. And that’s exactly what happened when a design flaw led to two fatal crashes involving the novel Boeing 737 Max aircraft.
On top of the tragic loss of life, the 737 was grounded for 20 months while federal aviation inspectors and Boeing investigated the cause of these errors, resulting in astronomical financial losses for the company to the tune of tens of billions of dollars.
Samsung Galaxy Note 7
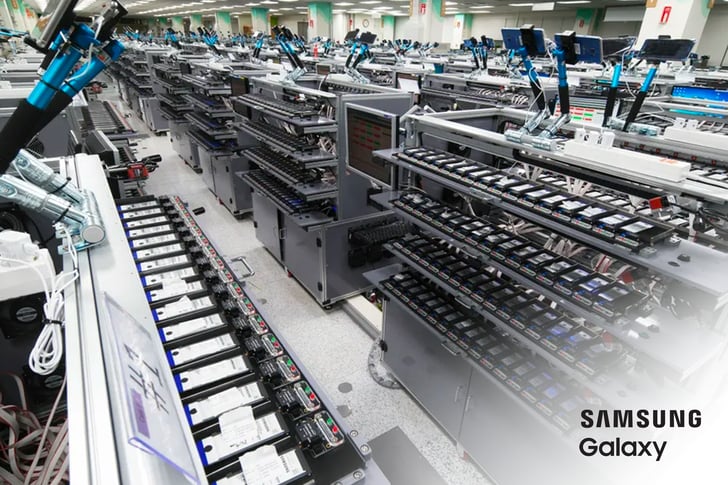

Samsung is a top-tier mobile technology company, but its reputation took a hit in 2016 when reports of the Galaxy Note 7 overheating and catching fire began pouring in. Both issues were related to defects in the lithium-ion battery of the phone.
The company subsequently recalled the phones and offered replacements to customers.
But even those replacements suffered a similar issue and production on the phones was halted altogether. Company profits plummeted as a result of the bad press related to these defects.
Takata Airbags
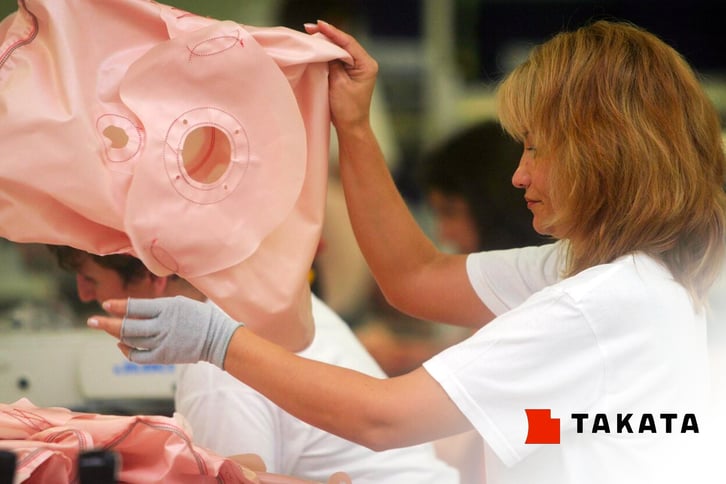

Takata has had an ongoing issue with defective products dating back to an original recall in 2013, as a result of airbag inflaters exploding.
Over the next eight years, the recalls just kept coming and ended up affecting over 40 million vehicles from 19 different manufacturers.
This product defect is a great example of why it's important to have great oversight on parts of the production process that are outsourced, as none of these manufacturing companies produced the faulty airbags themselves.
This fact did not prevent the public from associating the negative press with the vehicles involved in the accidents, however.
Contacting a Manufacturing Defect Expert
For large or complex organizations, the task of reducing manufacturing defects may seem overwhelming. But that doesn't make it any less important.
If the goal of manufacturing is to produce high-quality, useful products that consumers are willing to purchase again and again, nothing could be more important than guaranteeing a successful process for producing those products.
Companies may need to employ the use of manufacturing defect experts to help the company in the event of litigation related to product defects.
A manufacturing company needs to be prepared for all outcomes related to the potential defectiveness or failure of its products.
The company could be held liable for damages or injury related to the use of their products, and having an expert on your side can be invaluable when facing liabilities.
There are different categories of experts that a company may need to employ, and it will need to choose one with expertise targeted to the type of manufacturing a company engages in.
-
Manufacturing experts – Can testify about defects that occur during the manufacturing process itself. Companies employ these experts to prove that injuries were related to improper use of a product and not as a result of a defect itself.
-
Engineering Experts – These experts are employed to testify about the designs and engineering employed during the concept of a product.
-
Accident Experts – Can reconstruct an accident to discover if the fault lies with a company or with a consumer. These experts are especially useful to automobile manufacturers.
-
Medical Experts – Can testify about medical products, or simply investigate potential causes of injury sustained by a plaintiff.
Strategies for Reducing Defects in Manufacturing
Reducing manufacturing defects will require that companies employ specific strategies through every step of the process.
A proactive approach to identifying potential issues before they occur can save a company from financial losses, lowered productivity, and possible litigation from defective products that make it through safeguards and reach consumers.
Below are listed some strategies companies should consistently implement to guarantee a continuous focus on identifying and rectifying product defects:
1. Proper Quality Management
Have specific and easy-to-follow standards and policies regarding checking the quality of suppliers, outsourcing agents, and every step of the manufacturing process.
2. Maintain a Positive Work Environment
Happy and engaged employees who share in the success of a process are less likely to engage in activities that could unintentionally lead to mistakes that result in product defects.
3. Aim For Continuous Improvement
Analyze every step of a manufacturing process, from the attainment of raw materials, through the process itself, all the way to the packaging and marketing strategies involved with each product.
4. Investigate Solutions for Every Issue
Every product defect, or potential product defect, deserves individual attention and must have a thorough solution put in place to prevent future issues.
5. Embrace Technology and Automation
Utilize ERP systems, IIOT, and model and data-driven machine learning to streamline processes. Implement automated systems to replace any process that is ripe for defects from human error.
6. Focus on Compliance
Build a company culture of compliance regarding production standards, and stress the importance of product quality and safety as a way to better serve customers.
7. Gather Employee Feedback
The workforce of a manufacturing company has in-depth knowledge and experience of the process, materials, and machinery used in manufacturing each product. Have face-to-face conversations with employees on the plant floor, and implement an employee suggestion program to encourage workers to speak up on potential problems.
8. Monitor Progress
Correcting a product defect is not a one-and-done process. Results must be continually quantified and policies frequently revisited to identify inconsistencies and further possibilities for improvement.
9. Uphold Maintenance Schedules
Maintain focus on performing consistent maintenance schedules and frequent inspections of machinery, processes, and product results.
10. Perform Testing
Utilize advanced technology to perform in-depth testing of products and how they would be affected by differing scenarios, such as environmental or temperature changes.
Tips to Remember When Reducing Defects in Manufacturing
 We’ve discussed the importance of proactively seeking solutions for reducing manufacturing defects. But a manufacturing company is a complex machine unto itself, and it cannot lose focus on the things that garner success overall.
We’ve discussed the importance of proactively seeking solutions for reducing manufacturing defects. But a manufacturing company is a complex machine unto itself, and it cannot lose focus on the things that garner success overall.
That is to say, one cannot seek to rectify defects at the expense of efficiency or productivity. They also cannot sacrifice the quality of a product to increase that productivity.
Instead, a company must find an acceptable balance by expending time, energy, and resources on every aspect of production.
So how does a company find that balance?
It all comes down to prioritizing goals.
Producing quality products must be at the top of the list, so sacrificing anything that jeopardizes that goal should be considered a hindrance.
Instead of trading one for the other, companies must be creative in finding solutions that offer a balance of both. Expending time and resources toward producing higher quality products should be a streamlined and efficient process in and of itself.
Tips for Reducing Manufacturing Defects
-
Don’t sacrifice quality for increased productivity. A company that does this is fighting against itself, as a lowered standard of quality will result in a lowered efficiency anyhow.
-
Maintain positive communication between design, engineering, and production departments. Keeping an open dialogue between all departments involved in the development and production of a product will allow the exchange of ideas and empower employees to work together to solve problems.
-
A focus on training cannot be overstated as it relates to product defects. This applies to every worker in the production line, including developers, engineers, and supervisors. Train the workforce to be as proactive as the company is when it comes to quality control to prevent having to circle back and fix errors related to a lack of knowledge or skills.
-
Develop and reinforce a culture of continuous improvement, so that every worker in the company understands and upholds the commitment to creating high-quality products, and is constantly striving to identify areas that could be improved.
-
Analyze software requirements and revisit coding before production begins, and periodically throughout the production process. Identifying potential issues before they escalate into defects is key. Utilize a double fault method to ensure mistakes are not made at this level to prevent defects down the line.
-
Invest in error monitoring software. The future of manufacturing is automated, and detecting and preventing defects and errors is one task that lends itself toward the implementation of technology. Real-time error monitoring systems and automatic exception reporting draw attention to where it's needed.
Final Thoughts On How To Reduce Defects in Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies have a goal of serving customers by producing high-quality products. They make a promise to the consumer that their products will perform as expected, and do so without risk of injury, illness, or failure.
A successful company needs to be smart and strategic in its efforts to reduce manufacturing defects. It will benefit both the company, the bottom line, and the rate of customer satisfaction.
The future of manufacturing is changing faster than it ever has. Advancements in automation, cloud computing, and new smart factories give companies an upper hand while facing the future of manufacturing. The companies that will be successful over the next decades are those that are able to adapt and improve using technology.

Written by Leslie Bloom
Related Posts
The New Playbook for Operational Learning and Development
How Dozuki empowers training leaders to close skills gaps, accelerate onboarding, and enforce standard work at scale. Training is No Longer a Department, It's a System ...
Continue Reading →Rethinking MES in the Era of the Connected Workforce
Most Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) were built to rigidly enforce processes, not to empower people or evolve how work gets done. MES platforms excel at orchestrating...
Continue Reading →Dozuki Announces Record Breaking 2025
Dozuki in 2025: Cementing Global Leadership in the Connected Worker Category Dozuki, the pioneer of the Connected Worker Platform since 2011, today announced its most...
Continue Reading →